What is 5G network?
5G means the fifth generation of cellular wireless technology. It succeeds in 4G LTE networks and enables much faster download speeds, higher connection density and ultra-low latency compared to previous generations.
The official standard for 5G was set by 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), which completed the initial 5G specifications in 2018. Unlike 4G, which requires the construction of new cell towers, 5G uses existing infrastructure and also operates on new radio frequency bands. , including mmWave (millimeter wave).
The jump from 4G to 5G is a huge leap forward – we're talking peak download speeds of 20Gbps*, compared to 1Gbps on a 4G network. Latency is also reduced to just 1-2ms versus 20-70ms on 4G network.
* “Gbps” means gigabit per second, which is a unit of measurement for data transfer speeds. Refers to the number of billions of bits of data that can be transferred in one second.
So, what does 5G mean in practical terms? This means 5G can handle significantly more data traffic, paving the way for transformative technologies like self-driving cars, IoT devices, 4K/8K video streaming, AR/VR applications, and more.
How does 5G technology work?
5G technology uses a variety of wireless spectrum bands and technologies to achieve ultra-fast speeds and low-latency connectivity:
● Sub-6GHz and mmWave.Radio frequencies used for 5G include sub-6GHz (below 6GHz) which provides a good coverage area and also mmWave (24-40GHz) which provides huge bandwidth for ultra-fast speeds.
● Advanced antenna systems. 5G technology uses MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) antenna technology allowing simultaneous communications through multiple antennas. This increases capacity and density.
● Small cell networks. 5G technology will rely heavily on small cell networks, which are compact base stations that can be mounted on lampposts, rooftops, etc. This provides local capacity boosts.
● Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA). This modulation technique allows efficient use of spectrum so that multiple users can access the network simultaneously.
● Network slicing. This allows mobile network operators to create multiple virtual networks over a shared physical infrastructure, tailored to specific applications or customers.
● Edge computing. Processing data closer to the user via small data centers reduces latency. This complements the speed of 5G.
Who invented 5G technology?
The development of 5G technology has been driven by extensive collaboration between telecom companies, academic institutions and technology standards organizations around the world. “Who created 5G?” While no single entity can claim to have “invented” 5G, some of the major contributors include companies like Ericsson, Nokia, Qualcomm, Samsung, Huawei, and ZTE, who have each invented important components of 5G networks. International bodies such as 3GPP and ITU have been instrumental in shaping 5G standards. At TDK, we focus on developing advanced materials and components such as ultra-small DC-DC converters and LTCC AiP devices for 5G small cell base stations. These innovations are integral to enhancing 5G network speeds and connectivity. Our commitment is reflected in initiatives such as Beyond 5G, where we aim to expand the capabilities of 5G technology and contribute to its future developments.

How fast is 5G Internet?
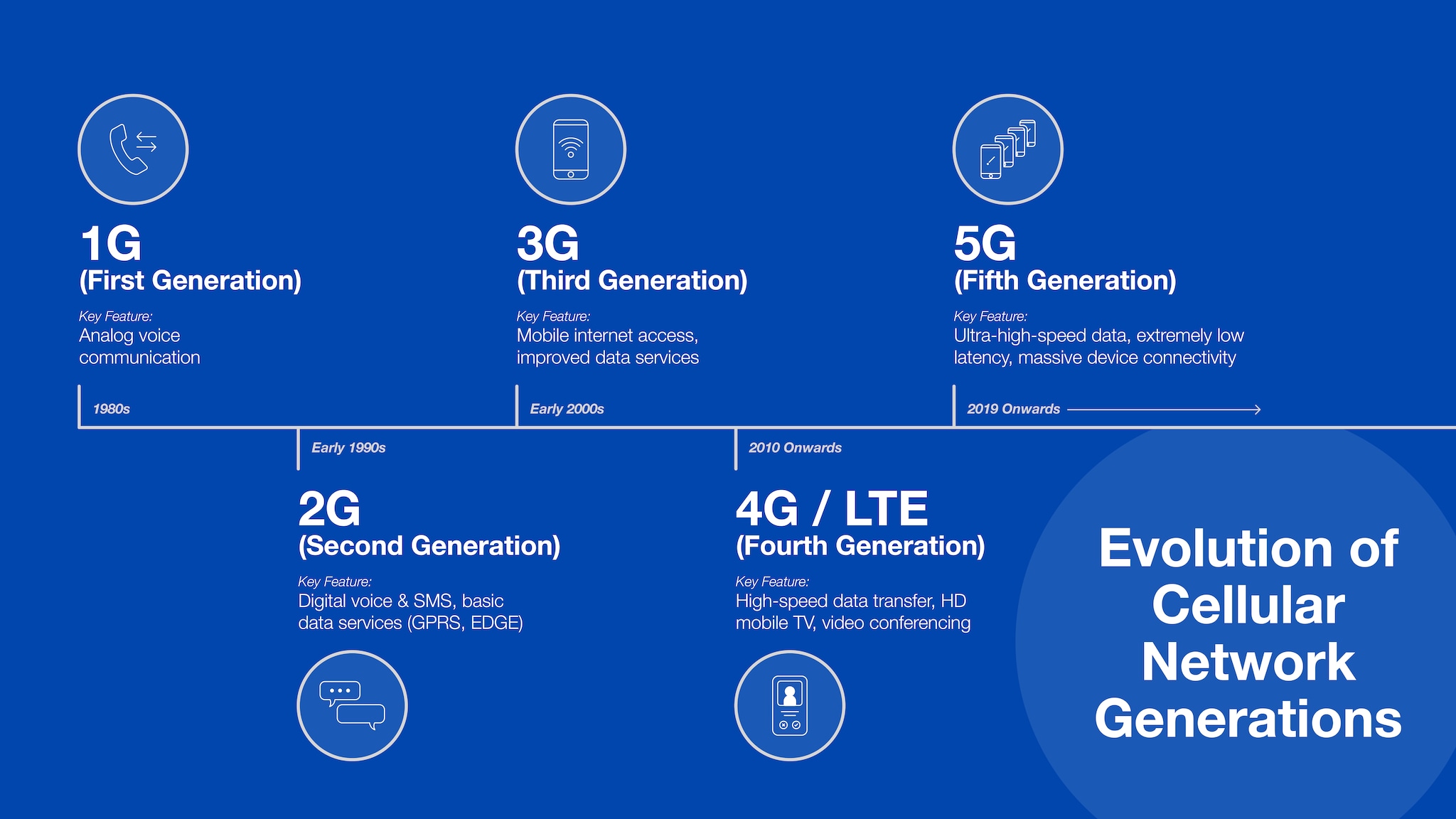
The launch of 5G technology represents a major leap forward compared to previous cellular network technologies. Each successive generation offered higher speeds and greater capabilities. To understand why 5G is better, let's review the development:
● 1G networks in the 1980s were analog systems designed primarily for voice calls. There was no encryption, so security was poor. Loading speeds were almost nonexistent.
● 2G networks, introduced in the 1990s, were the first to digitize signals to improve security and data services such as text messaging. However, the maximum speed was only 64 kbps. A 3-minute song can take more than 20 minutes to download!
● 3G brought mobile internet into the mainstream when it launched in the 2000s. But access speeds were still very slow by today's standards, ranging from 384 Kbps to 2 Mbps. Streaming video or music was not practical.
● 4G LTE, first deployed in 2010, was the first network fast enough for advanced applications, streaming high-definition video, and downloading large files. Theoretical maximum speeds reached 100Mbps but were often much lower in reality.
Now with 5G technology, we are entering a new era. How fast is 5G compared to 4G? 5G technology works on new radio frequency bands that can transmit more data. 5G technology uses shorter transmission bursts to reduce latency to just a few milliseconds. This enables real-time communication of smart devices.
In terms of speed, 5G technology is superior to its predecessors. 5G achieves ultra-fast download speeds of up to 20 Gbps, compared to 1 Gbps on 4G. It takes 26 hours to download a Full HD movie on a 3G network, compared to just 3.6 seconds on a 5G network!
Is 5G better than LTE? definitely! The benefits of 5G are wide-ranging, from dramatically increasing data speeds and reducing latency to enhancing network reliability and capacity, paving the way for transformative changes in sectors such as healthcare, manufacturing and transportation.
Is 5G better than 4G? Without a doubt, yes. 5G delivers a 10 to 100X improvement over 4G across every metric. From speed to capacity to reliability, 5G represents a radical upgrade.
The capabilities of 5G enable a world of seamless connectivity and real-time automation that previous generations could not match. Exploring why 5G matters reveals its critical role in the next wave of technological innovation; It's not just about faster speeds, it's also about enabling real-time data processing, connecting billions of devices, and unleashing the potential of smart cities and autonomous technologies. While previous generations connected people, the fifth generation will connect the world.
Looking to the future, the foundation laid by 5G technology paves the way for future developments such as 6G, which will further expand these capabilities and capabilities.
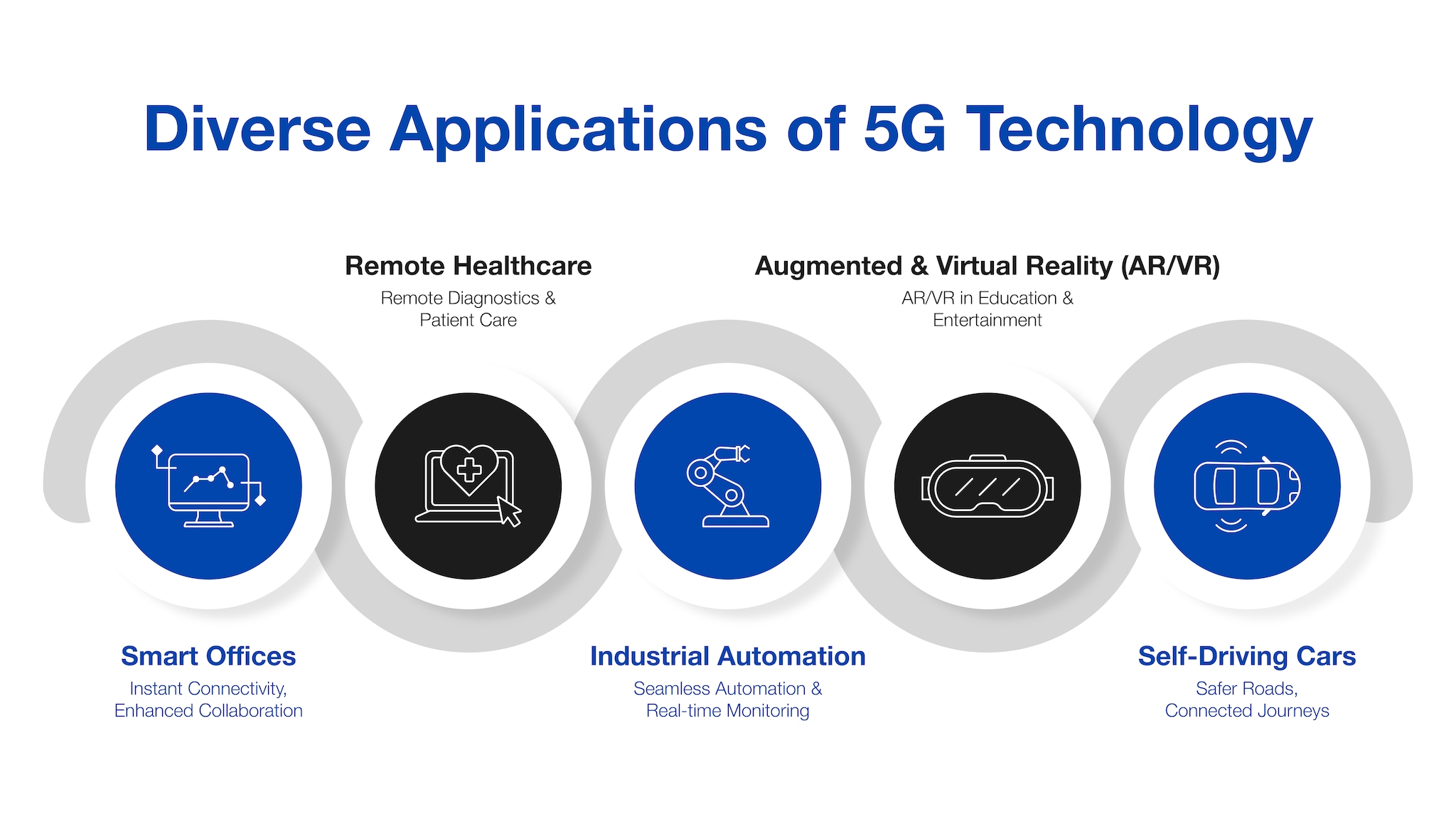
What will 5G enable? Explore its impact across different fields
With its ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and ability to support massive device densities, 5G will enable advanced new applications in many areas of business, government and everyday life.
● In the business world, 5G technology opens the door to smart offices, remote collaboration and workers with the help of augmented reality and real-time analytics. Commercial use cases for 5G technology include connected logistics, robotics and remote control of machinery or vehicles. Retail, healthcare, finance and most industries will benefit.
● For governments and cities, 5G will “change the world” by supporting the massive deployment of smart infrastructure – from smart grids to smart traffic systems and environmental monitoring through IoT sensors. Consumer use cases for 5G mean ultra-fast mobile broadband for households, better community services, and new consumer applications.
● In healthcare, 5G technology allows remote patient monitoring, remote healthcare consultations, and remote surgeries. Doctors can access or update medical records in real time. Wearable devices continuously upload health data via 5G.
● Industrial manufacturing will use 5G technology for automation, traceability, quality control and coordination across global supply chains. Sensors will monitor equipment and infrastructure 24/7 and help improve productivity.
● 5G technology will provide highly immersive augmented and virtual reality experiences in retail, education, design, entertainment and more. Interactive shopping with augmented reality, virtual tours and 3D product displays will become mainstream.
● Self-driving vehicle technology relies on 5G connectivity for navigation, obstacle detection, route planning, and communication with other vehicles. This will make self-driving cars practical.
For consumers, “How will 5G affect me?” You can expect almost instant downloads, the ability to stream 8K video anywhere, and responsive online gaming. Augmented reality apps will enable new ways to shop, learn and explore. However, it is important to be aware of potential drawbacks such as the need for more infrastructure such as cell towers, potential network security concerns, and higher costs for 5G-compatible hardware. Additionally, full global availability of 5G technology may take some time, leading to unequal access in the initial stages.
5G is a transformative technology that will impact almost every industry and change the way we live, work, shop and entertain. It will enable smart cities, automation across factories and workplaces, self-driving vehicles, remote healthcare, and endless applications that we can't even imagine yet. 5G truly represents the next giant leap in connectivity.
Conclusion
The dawn of 5G represents a huge leap forward in wireless technology. With ultra-fast speeds, ultra-low latency, and the ability to support millions of devices, 5G will truly herald the next era of connectivity. This revolutionary technology will lay the foundation for emerging innovations like self-driving cars, smart cities, telehealth, and technologies we can't even imagine yet. While previous generations connected people, the fifth generation will connect the world. By working together to embrace the enormous potential of 5G, we can build a more efficient, empowered and automated future. The possibilities are endless as we stand on the cusp of this new, hyper-connected era.

