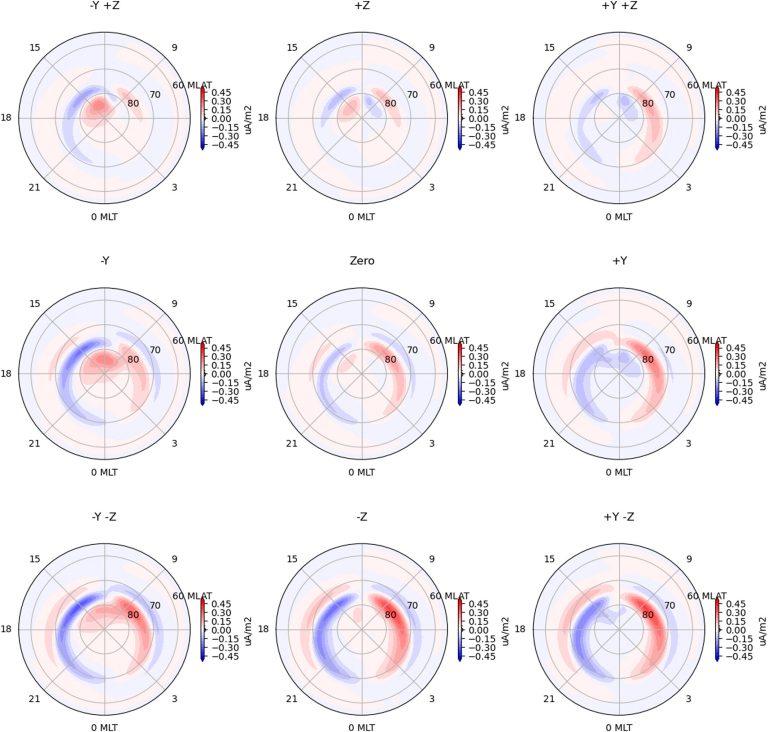
The steady-state conditions of the pattern of the Arctic auroral current system (polar visibility), which vary with the direction of the solar wind magnetic field, can be reproduced almost perfectly by SMRAI2. Red and blue represent ground (downward) and upward currents, respectively; Y and Z represent the direction of the magnetic field of the solar wind, where Z is positive north in the north-south direction and Y is positive west in the east-west direction. For example, “zero” indicates no Y and Z components of the solar wind's magnetic field, “-Z” indicates a fully southerly direction, and “-Y -Z” indicates a southeasterly direction. credit: Space climate (2024). doi: 10.1029/2023SW003720
× Close
The steady-state conditions of the pattern of the Arctic auroral current system (polar visibility), which vary with the direction of the solar wind magnetic field, can be reproduced almost perfectly by SMRAI2. Red and blue represent ground (downward) and upward currents, respectively; Y and Z represent the direction of the magnetic field of the solar wind, where Z is positive north in the north-south direction and Y is positive west in the east-west direction. For example, “zero” indicates no Y and Z components of the solar wind's magnetic field, “-Z” indicates a fully southerly direction, and “-Y -Z” indicates a southeasterly direction. credit: Space climate (2024). doi: 10.1029/2023SW003720
There are three levels of intensity of space storms: geomagnetic storms, solar radiation storms, and power outages. These storms produce various impacts on Earth, including problems with satellites, GPS, communications, and the electrical grid, as well as health risks to astronauts and people traveling at high altitudes. Geomagnetic storms also produce beautiful auroras that are commonly observed in the polar regions.
Because of the potential negative effects of space storms, researchers have developed physics-based models that predict the auroral stream system based on incoming solar wind particles emanating from the Sun.
However, up to this point, these models have been slow and require a super-fast computer to run. Researchers have now created a machine-learning-based simulator that simulates the physics-based auroral stream system much more quickly and with less computing power.
The team published the results of their study in the journal Space climate.
“Physics-based simulation of the auroral stream system is an option for space weather forecasting,” said Ryoho Kataoka, first author of the paper and an associate professor at UCLA. “However, we need a dedicated supercomputer to run the physics-based simulation.” National Polar Research Institute and SOKENDAI, both in Tachikawa, Japan.
“One such model is REPPU (REProduce Plasma Universe), which is a well-known and reliable model that reproduces the auroral stream system. Once we created the 'simulator,' we could get similar results using a laptop.”
The new simulator model, the Alternative Model for the REPPU Auroral Ionosphere Version 2 (SMRAI2), is a million times faster than physics-based simulations and incorporates seasonal effects into its model.
While solar weather forecasts cannot change the effects of solar radiation and solar wind particles on and around Earth, they can help communities affected by solar weather prepare for communications difficulties and failures and limit radiation exposure to astronauts and high-altitude aircraft passengers.
Satellites, in particular, are very sensitive to drag caused by magnetic storms. In fact, 38 commercial satellites were lost in February 2022 due to re-entry into Earth's atmosphere after a moderate magnetic storm. These magnetic storms are the result of the transfer of significant energy from the solar wind into the Earth's magnetosphere.
By giving the complex variations of the solar wind already observed, the very complex temporal variations of the auroral jet streams can also be reproduced. Light colors represent observed values, while dark colors represent predictions by SMRAI2. The au obs and al obs are observed with AU and AL indices, and au esn and al esn are AU and AL indices calculated from the simulator results. The AU and AL indices indicate auroral activity at high latitudes. credit: Space climate (2024). doi: 10.1029/2023SW003720
× Close
By giving the complex variations of the solar wind already observed, the very complex temporal variations of the auroral jet streams can also be reproduced. Light colors represent observed values, while dark colors represent predictions by SMRAI2. The au obs and al obs are observed with AU and AL indices, and au esn and al esn are AU and AL indices calculated from the simulator results. The AU and AL indices indicate auroral activity at high latitudes. credit: Space climate (2024). doi: 10.1029/2023SW003720
The research team used a time-based machine learning model called an Echo State Network (ESN) to create a physics-based prediction model simulator. Most importantly, ESNs are a type of recurrent neural network designed to efficiently handle sequential data.
The current study has already improved with the initial release of the ESN-based simulator, version 1.0. The team trained the new simulator model, SMRAI2, using a larger number of physics-based simulation outputs than the original version 1.0 model.
“The product of this study, SMRAI2, is the first example of auroral physics that uses machine learning technology to simulate ionospheric outputs for a physics-based global magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) simulation,” Kataoka said. “Collecting more MHD simulation data and using other state-of-the-art models will enable us to Machine learning to update prediction accuracy in the near future.” MHD simulations are designed to describe the behavior of the magnetosphere, where the solar wind interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field.
The next step for the research team is to integrate the simulator into running the Space Weather Forecast Suite, a collection of forecasts that provides a range of future predictions of space weather. Their ultimate goal is to use the simulator, along with several observational datasets, in data assimilation forecasts, which integrate model output and observations to improve forecast accuracy.
more information:
Ryoho Kataoka et al., Machine learning simulator for physics-based simulation of the auroral stream system, Space climate (2024). doi: 10.1029/2023SW003720
Magazine information:
Space climate
Provided by the Information and Systems Research Organization