There is no doubt that the emergence of generative AI models will significantly disrupt the future of the entertainment industry. This week, a new report laid out just how disruptive Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) will be for artists over the next three years.
The report (downloadable here as a PDF) warns that GenAI “signals a broad transition from existing technologies to new processes” and is likely to “rebalance demand for labor and capital across entertainment industries.”
For creative workers, this means they will face “an era of disruption, defined by the consolidation of some job roles, the replacement of existing job roles with new ones, and the elimination of many jobs entirely.”
The survey was conducted by consulting firm CVL Economics and jointly commissioned by the cartoon guild IATSE Local 839, the Conceptual Art Society, the Human Art Campaign, and the National Cartoonists Society Foundation. It surveyed 300 executives from six entertainment industries, including CEOs, senior executives and mid-level managers. Conducted between November 17 and December 22, 2023.
GenAI is not a future technology – it exists today
It's easy to conclude from the study that GenAI is not a hypothetical technology that could impact film, game, and VFX artists at some point in the future. It is available now It turns the entertainment industry upside down today. In fact, two-thirds of the 300 business leaders surveyed expect GenAI to play a role in enhancing or replacing current job titles in the next three years (2024-2026).
An estimated 204,000 jobs in the entertainment industry will be significantly disrupted by generative AI Over the next three years. This figure does not include freelancers and contract workers, so the actual number of jobs cut is likely to be larger than the survey range. (The report considers functionality to break down when “a sufficient number of tasks are merged, replaced, or eliminated by GenAI.”)
Of the 204,000 jobs affected, 118,500 of them are in the film, television and animation industries, representing 21.4% of the 555,000 jobs in the three fields. An additional 52,400 jobs are out in the gaming industry, representing 13.4% of the 390,500 employees in the sector.
The most affected state is California, the center of the American entertainment industry, which will see 62,000 creative jobs affected, followed by New York (26,000 jobs) and Georgia (7,800 jobs).
How open are entertainment companies to using AI?
Entertainment executives are literally frothing to start implementing GenAI into their pipelines. Ninety-nine percent of people who participated in the survey said they plan to implement artificial intelligence in the next three years. In fact, a quarter of companies surveyed indicated they already have one or more GenAI programs, while 15% said they had concerns about GenAI programs and would not implement them until these issues were resolved.
One percent of survey respondents said they do not plan to use GenAI within the next three years.
Who will be affected first?
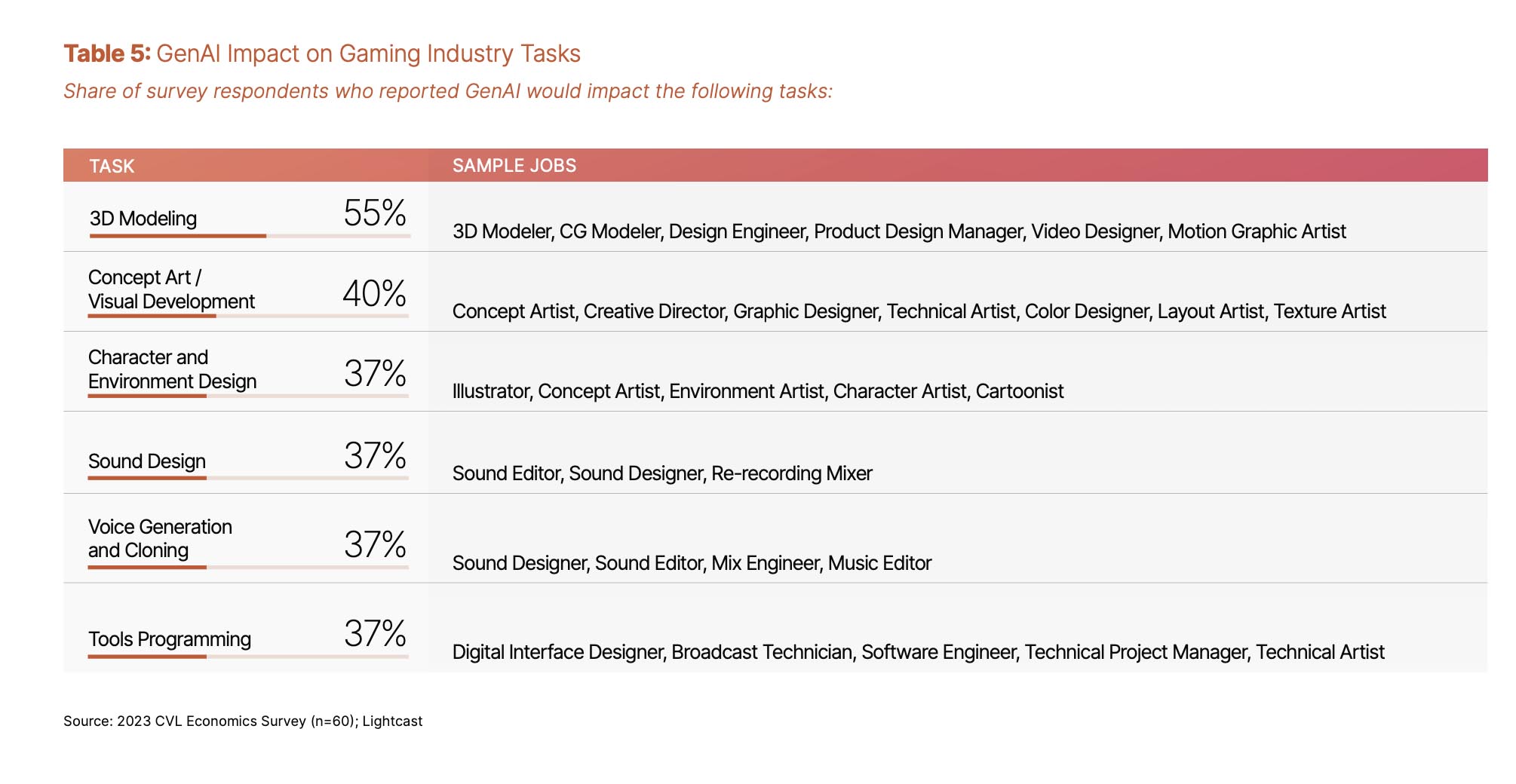
Some jobs in the animation and visual effects industries will be affected more than others. For example, of the quarter of companies that have already implemented GenAI programs, 44% use the technology to help create 3D models while 39% create character and environment design tasks.
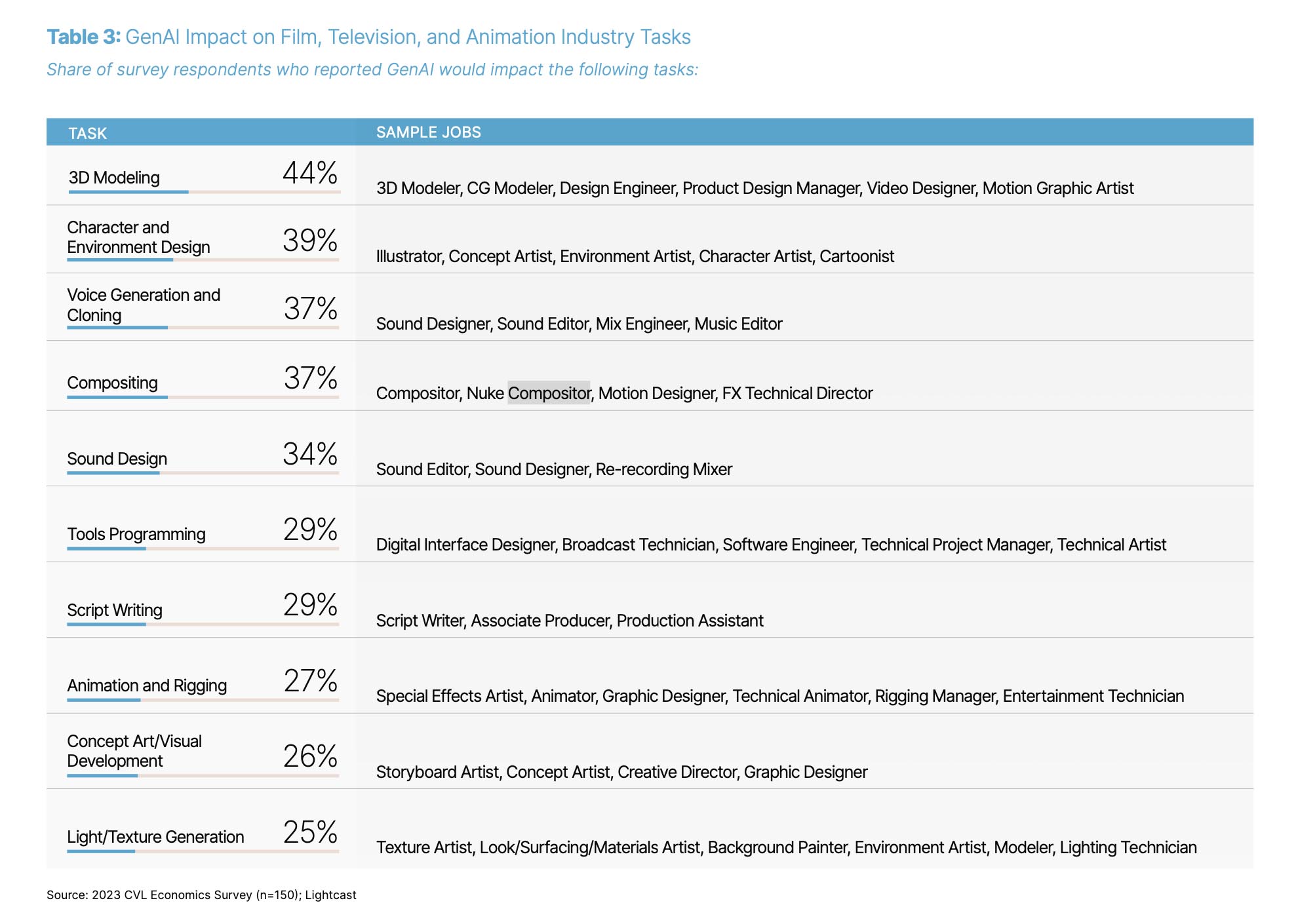
Furthermore, 33% of survey respondents expect 3D modelers to be impacted in the next three years, while 25% believe installers were at risk over the same time period. Only 15% said that storyboarders, animators, illustrators, and form/surface/material artists will face job displacement by 2026.
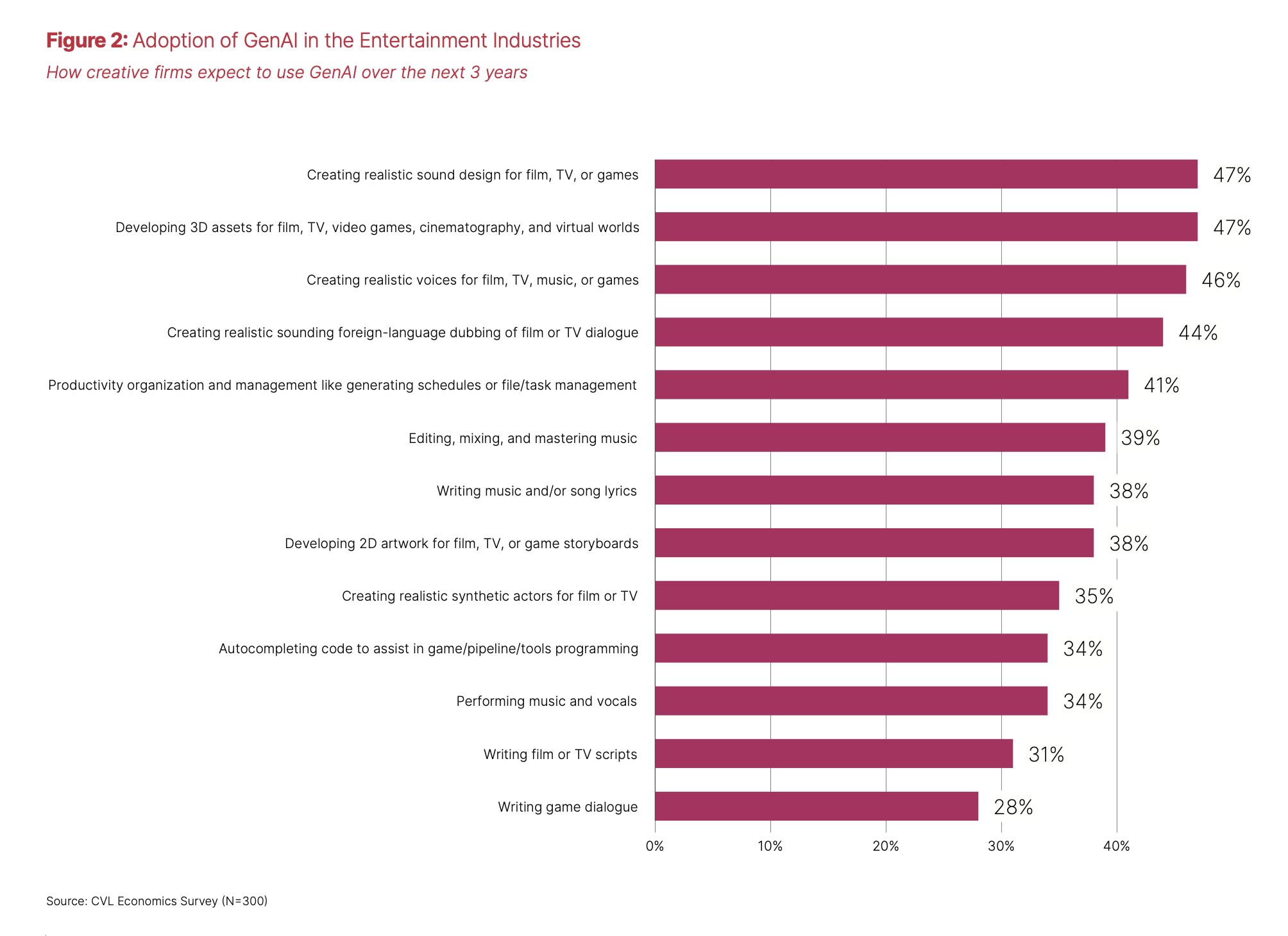
Equally revealing is how entertainment companies plan to use GenAI. Nearly half (47%) expect to use it to develop 3D assets, while 38% will use it for 2D concept art and storyboards. Thirty-five percent want to use it to create animated characters (prosthetic actors, in their terminology) for film/TV, while 31% want to use it to write scripts.
More takeaways and conclusion
For its part, The Animation Guild released a list of the report's key findings, which included some surprising responses:
- Three-quarters of respondents said GenAI tools, software, and/or models have already supported eliminating, reducing, or consolidating jobs in their business division.
- More than 90% of respondents believed GenAI would play a larger role in the entertainment industry, although only 26% of survey respondents felt their company was fully prepared to integrate GenAI into their workflow.
The report ends with this suggestion for entertainment industry decision-makers:
The future has not yet been written, and it does not have to be created by artificial intelligence. It is important to remember that GenAI's outputs are limited by its inputs. If responsibility for content creation shifts from humans to machines, which currently can only formulate output based on previously created content, the availability and uniqueness of new content brought into the world will become more limited. It is crucial that those in leadership positions, especially in the entertainment industries, keep this at the forefront of their minds and think about the ways in which new technologies can expand human creativity, not replace it.

