In an ever-evolving technology landscape, staying ahead of the curve is vital for businesses, governments and individuals alike. To help you navigate this dynamic field, we've put together a comprehensive exploration of ten strategic technology trends shaping the future. These trends include the areas of artificial intelligence (AI), cybersecurity, biotechnology, immersive experiences, and more.

Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI)
clarification: Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) is an important aspect of artificial intelligence (AI) that seeks to enhance the transparency and explainability of artificial intelligence systems. In a world where artificial intelligence impacts many aspects of our lives, from healthcare to finance, it is essential to understand how AI systems make decisions. XAI technologies enable users to understand and trust AI-based predictions by providing transparent interpretations of model outputs.
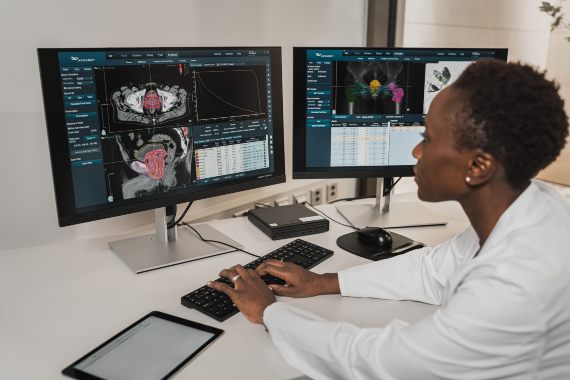
Example: Imagine healthcare AI that helps doctors diagnose diseases based on medical imaging. XAI ensures that the AI not only provides a diagnosis, but also explains the specific features it took into account to reach that conclusion, giving medical professionals the confidence to make informed decisions.
Zero Trust Security
clarification: The Zero Trust Security program is considered a quantum leap in the field of cybersecurity. Traditionally, network security has operated according to a “trust but verify” model, but in the era of increasing cyber threats, this approach is no longer sufficient. Zero Trust Security assumes that no entity should be trusted, whether inside or outside the network. It emphasizes constant verification of users and devices, regardless of their location or network connection, effectively creating a security perimeter around every device and user.
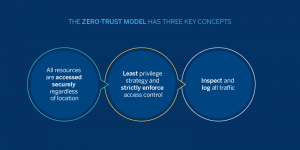
Example: The company applies a Zero Trust Security framework to protect its sensitive data. Every employee, whether working from the office or remotely, is continuously verified before accessing company resources, reducing the risk of a data breach.
Biotechnology developments
clarificationBiotechnology includes a wide range of innovations in the fields of biology and genetics. One of the most transformative developments is CRISPR-Cas9, a gene editing technology that allows precise modification of DNA. This technology has implications for medicine, agriculture and environmental conservation.
ExampleIn medicine, CRISPR-Cas9 is used to treat genetic diseases by editing the patient's DNA. In agriculture, it enhances crop productivity and disease resistance through genetic modification, and in environmental conservation, it can be used to modify organisms to clean up pollution.
Experiential marketing through immersive technologies
clarification: Experiential marketing is being revolutionized by the integration of immersive technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). These technologies enable brands to engage customers on a much deeper level, delivering memorable and interactive experiences.
Example: Retailers are using augmented reality apps that allow customers to virtually try on clothes or visualize how furniture and decor items will fit in their homes. This immersive experience enhances customer engagement and helps drive purchasing decisions.
Exoskeletons and human augmentation
clarification: Exoskeletons and human augmentation technologies are wearable devices that enhance human capabilities. They find applications in industries such as manufacturing, where they can reduce physical stress, and in health care, aiding in rehabilitation and mobility for individuals with disabilities.

Example: In manufacturing, workers can wear exoskeletons to help with heavy lifting and repetitive tasks, reducing the risk of injury and increasing productivity. In health care, it helps individuals with mobility disabilities regain the ability to walk.
Distributed cloud computing
clarification: Distributed cloud computing represents an evolution in cloud technology. It allows cloud resources to be deployed across multiple locations while still being managed centrally. This approach reduces data latency and enhances accessibility by placing and processing data closer to end users or devices, making it ideal for applications that require low-latency access.
Example: In the world of online gaming, distributed cloud computing allows players to experience low-latency gameplay, regardless of their geographic location. Data and processing are optimized for a smooth gaming experience.
Neural computing
clarification:Neurocomputing is an emerging field inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. It aims to create more efficient and brain-like processing. Neural chips process information in a similar way to neurons, which could improve the efficiency and adaptability of AI systems.

Example: Neural computing has the potential to revolutionize robotics by enabling robots to process sensory information in a way that is closer to human cognition. This could lead to the creation of robots that are more intuitive and adaptable to different tasks.
Biometric authentication and privacy
clarification: Biometric authentication uses unique biological or behavioral traits, such as fingerprints or facial features, to verify a user's identity. Although it is highly secure, it is necessary to ensure the privacy and security of biometric data.
Example: Mobile devices use biometric authentication, such as facial recognition or fingerprint scanning, to open and authorize payments. These systems store biometric data securely, encrypt it, and adhere to strict privacy regulations to protect user privacy.
Circular economy technologies
clarificationCircular economy technologies promote sustainability through reuse and recycling of materials. They include innovative recycling processes, sustainable materials, and 3D printing using recycled plastic, ultimately reducing waste and contributing to a more environmentally friendly approach to manufacturing and consumption.
Example: One company is adopting 3D printing technology that uses recycled plastic. This not only reduces waste, but also reduces the environmental impact associated with plastic production.
Quantitative statistics
clarificationQuantum computing is a revolutionary technology that harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform complex calculations at unprecedented speeds compared to classical computers. Quantum bits (qubits) can exist in multiple states simultaneously, enabling quantum computers to address problems that were previously considered unsolvable.

ExampleQuantum computing has the potential to disrupt various industries, such as cryptography. Large-scale quantum computers could break existing encryption methods, making data more vulnerable unless new quantum-resistant encryption techniques are developed.
Incorporating these strategic technology trends into your business strategy or understanding their implications for your industry is essential to staying competitive and relevant in today's rapidly changing technology landscape. Each of these trends represents an important step forward in the world of technology, and their impact will continue to shape the way we live and work in the years to come.
Written by Ahmed Banafa
Coverage: Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, Blockchain and Quantum Computing