Main take:
- Non-controlling interests (NCI) are when someone owns less than half of the shares without decision-making power, and is valued on the basis of net assets.
- Many public shareholders have a small stake, usually 5% to 10%, while others have greater control and voting rights.
- Non-controlling interests can be direct (pre- and post-acquisition equity) or indirect (post-acquisition equity) interest in the consolidated financial statements.
- Activist investors who own large shares can impact financials positively, influencing operational improvements, restructuring, and environmental/social policies.
Have you ever thought what a non-controlling interest is? Why should you learn more about it as a true expert?
Non-controlling interest means owning less than 50% of the shares and no decision-making power. These interests are valued on the basis of the net assets of the entity and do not take into account potential voting rights.
Most shareholders in public companies have a small ownership stake; Even 5% to 10% is important. This contrasts with controlling or majority interests, where investors have voting rights and influence over company decisions.
Non-controlling interests in the consolidated financial statements
Holders of common stock in the parent company have certain rights. These rights include receiving cash dividends based on profits and voting on important decisions regarding assets and liabilities.
These decisions can include matters such as mergers or sales of subsidiaries. Non-controlling interests can be classified as direct or indirect in the consolidated financial statements.
Direct non-controlling interests refer to the involvement of subsidiary equity before and after the acquisition. On the other hand, indirect non-controlling interests only involve sharing the ownership rights of the subsidiary after the acquisition.
Holders of common stock in the parent company have certain rights. These rights include receiving cash dividends based on profits and voting on important decisions regarding assets and liabilities.
Activist investors and their influence
Investors who receive large shares, typically 5% to 10%, can become active investors. This may result in them obtaining a recoverable non-controlling interest.
Their actions can significantly impact financial statements, promote positive change such as operational improvements, restructuring efforts, or influence environmental and social policy decisions.

These investors collaborate with company leaders, propose changes, and band together with fellow shareholders to exert greater influence.
This collaboration can impact consolidated financial statements and call for improvements and shifts in policy.
Example of non-controlling interest by a professional
The company buys 80% of XYZ shares, while minority shareholders own the remaining 20% of the company. Non-controlling interests represent the ownership interest of minority shareholders in the subsidiary.
Over time, goodwill initially recognized at the acquisition date is gradually charged, following accounting rules and subject to regular tests for potential losses.
Why is financial modeling so important?
Financial modeling is important. It ensures that the consolidated financial statements accurately present the net income of the subsidiary.
However, assume that both the parent and minority shareholders pay more than the fair value of the net assets acquired. In this case, any excess amount is recorded as goodwill in the consolidated financial statements.
This helps in calculating ownership shares in the subsidiary that are not attributable to the parent company.
What is good faith in this case?
Goodwill represents the additional expenses incurred when purchasing a company at a price above its fair market value. Over time, goodwill is recorded as an expense, following accounting rules and tested for potential losses.
As recognized by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), these accounting practices are consistent with the purchase and acquisition method of accounting.
What are non-controlling interests that are recoverable?
A redeemable NCI is a small ownership stake in a company held by investors with limited decision-making power. They can choose to sell their share later.
Non-controlling interests on the balance sheet – explained.
Now, let's take a closer look at the non-controlling interests on the balance sheet:
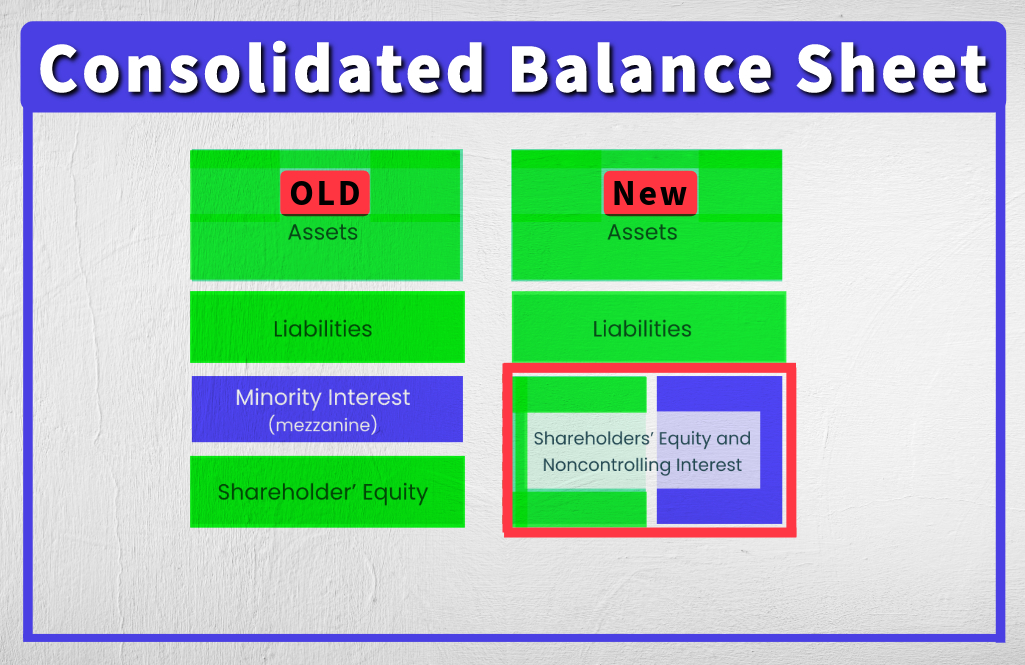
NCI is shown in the equity section of the parent company's balance sheet. It is separate from the parent company's equity, rather than between liabilities and equity.
It is necessary to clearly show and consolidate the parent's net income and non-controlling interests in the income statement.
Previously, net income of non-controlling interests was considered an expense when calculating consolidated net income.
Valuation of net acquired assets
Previously, when a company acquired a subsidiary without full control, it recognized only the fair value of the controlling interest.
Non-controlling interests are recognized at their carrying value. Non-controlling interests are recorded at book value.
Current rules provide for the net assets of a purchased subsidiary to be recorded at fair value, regardless of the level of controlling interest.
Example A – Purchase price allocation
Alpha purchased 80% of Sierra's stock for $22.00 in cash per share. Sierra's stock price averaged $20.00 per share in the three days following the purchase.
Transaction costs were $15, and Alpha's corporate tax rate was 30%. Sierra's pre-transaction financial results are consistent with its tax books and balance sheets.
The key question is how to calculate good faith using the old and new rules. We need to record the net assets of a subsidiary at their fair value, regardless of controlling or non-controlling interests.
How to calculate net income attributable to non-controlling interests?
- Determine the net asset value of shareholders' equity.
- Multiply the net asset value by the fraction that represents minority ownership.
- Document the result in the balance sheet.
minimum
Understanding non-controlling interests is critical for investors and financial professionals because it affects financial statements, valuation, and accounting practices.
Adherence to accounting rules and clarity in financial reporting is essential to accurately represent the interests of controlling and non-controlling stakeholders.

